India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor
This article provides detailed insights into the India-Middle
East-Europe Economic Corridor, which strives to set a business and
transportation corridor that spreads from India to Europe crossing West Asia.
India, the Middle East, and Europe are the key players in this project. Authored by Gaurav N,
this informative piece has undergone meticulous review by our highly qualified
faculty member, Kapil
Kushwah in preparation for publication on our website and in our current
affairs news.
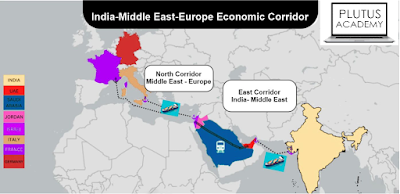
The India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor is a major
infrastructure and connectivity project aimed at establishing a trade and
transportation corridor that spans from India to Europe through West Asia. This
ambitious initiative has gained significant attention due to its potential to
revolutionize economic ties, transportation networks, and digital connectivity
across a vast Eurasian region. It is often seen as an alternative vision to
China's Belt and Road Initiative (BRI).
Key features of the India-Middle East-Europe Economic
Corridor:
Connectivity: The project envisions the construction
of a modern railway link that traverses the Arabian Peninsula. This railway
link is intended to seamlessly connect with existing shipping routes that link
India and Europe. The goal is to enhance the connectivity between these
regions, facilitating the movement of goods and people.
For the latest current affairs updates, students can
conveniently access our dedicated current affairs section on the Plutus Academy
website.
Alternative to BRI: This initiative is often regarded
as a counterbalance to China's BRI, which has been criticized for its
debt-driven financing and strategic implications. The India-Middle East-Europe
Economic Corridor offers an alternative approach to infrastructure development
and connectivity, emphasizing sustainability and economic integration.
Motivation From the past legacy: The corridor draws
inspiration from the historic Spice Route, which was a network of trade routes
that connected the East and West for centuries. In a modern context, it seeks
to revive and expand upon this historical trade and cultural exchange.
Participants: The initiative is jointly led by the
United States and India, with active participation from several countries,
including Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, Jordan, Israel, and the
European Union. These nations have signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU)
to establish the corridor, focusing on economic integration, connectivity,
logistics, clean energy production, and energy transmission infrastructure.
Strategic Significance: The corridor could have
strategic significance by offering an alternative transportation route to the
congested Suez Canal. By bypassing the Suez Canal, it aims to provide a more
efficient and reliable trade route between Asia, the Middle East, and Europe.
Green Hydrogen: The project places emphasis on green
hydrogen, indicating a commitment to clean and sustainable energy solutions.
This aligns with global efforts to address climate change and reduce carbon
emissions.
Infrastructure Development: The initiative aligns
with India's domestic initiatives such as Make in India, Sagarmala (a port-led
development program), and Atmanirbhar Bharat (self-reliant India). It aims to
promote infrastructure development and self-sufficiency in key sectors.
Global Infrastructure Investment: The project emerged
as part of the Partnership for Global Infrastructure Investment (PGII), a
US-led initiative. This underscores its significance in response to the global
demand for high-quality infrastructure financing, which could stimulate
economic development in multiple countries and sectors.
Take your preparation for exams, including IELTS, SSC, and
bank coaching in Delhi, to the next level with Plutus Academy. We focus on
creating a solid educational framework, delivering tailored guidance, and
offering accessible online learning options.
Overall, the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor is a
significant geopolitical and economic undertaking that has the potential to
reshape trade and connectivity in the Eurasian region while offering an
alternative model of infrastructure development to the world.



Comments
Post a Comment